Introduction

A. Definition of on page SEO
On page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to improve their visibility and rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs). It involves various techniques and strategies implemented directly on the website to enhance its relevance, user experience, and overall search engine friendliness.
On page SEO focuses on optimizing factors that are within the website owner's control, such as content, HTML source code, and website structure. By optimizing these elements, website owners aim to communicate the relevance and value of their content to search engines, ultimately improving their chances of ranking higher in organic search results.
B. Importance of on page SEO for search engine rankings
On page SEO plays a crucial role in determining a website's visibility and rankings in search engine results. Here are some key reasons why on page SEO is essential for achieving better search engine rankings:
- Relevance: Search engines strive to provide the most relevant results to users' search queries. By implementing on page SEO techniques, website owners can optimize their content and align it with the search intent of their target audience. This helps search engines understand the content's relevance and increases the likelihood of ranking higher for relevant search queries.
- User Experience: On page SEO focuses on improving the user experience by optimizing various elements such as page loading speed, mobile-friendliness, and content structure. Search engines consider user experience signals as an important ranking factor. A well-optimized website that offers a seamless browsing experience is more likely to rank higher in search results, leading to increased organic traffic and engagement.
- Organic Traffic: Higher search engine rankings result in increased organic traffic, as websites that appear on the first page of search results receive the majority of clicks and visibility. By implementing effective on page SEO strategies, website owners can improve their website's visibility, attract more organic traffic, and potentially generate more leads or sales.
- Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank higher in search results are often perceived as more trustworthy and credible by users. On page SEO helps establish trust and credibility by optimizing content, using proper formatting, providing valuable information, and ensuring a positive user experience. These factors contribute to building a strong online reputation and increasing the likelihood of attracting organic traffic and repeat visitors.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective on page SEO can give websites a competitive edge over others in the same industry or niche. By optimizing their web pages and content, website owners can surpass competitors in search rankings, gain more visibility, and capture a larger share of organic traffic. This advantage can lead to increased brand awareness, conversions, and business growth.
Keyword Research
A. Understanding the target audience and their search intent
Effective keyword research begins with a deep understanding of the target audience and their search intent. By comprehending the needs, preferences, and motivations of the target audience, website owners can identify the keywords and phrases they are likely to use when searching for relevant information or products.
To understand the target audience better:
Define the target demographics: Determine the age, gender, location, interests, and other relevant characteristics of the target audience.
Research their pain points: Identify the challenges, problems, or questions that the target audience may have related to the website's niche.
Study their language and preferences: Analyze the language, vocabulary, and phrases commonly used by the target audience when discussing the topic or industry.
B. Identifying relevant keywords and phrases
Once the target audience is understood, the next step is to identify relevant keywords and phrases that align with their search intent. Here are some strategies to identify such keywords:
- Brainstorming: Start by brainstorming potential keywords and phrases based on the knowledge of the industry, products, or services offered. Consider general terms as well as more specific long-tail keywords.
- Competitor analysis: Analyze the websites and content of competitors to identify the keywords they are targeting. Tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs can provide valuable insights into competitor keywords.
- Customer feedback and inquiries: Pay attention to customer inquiries, feedback, and comments to identify the language they use when discussing the topic or seeking information.
- Industry forums and communities: Participate in industry forums, social media groups, and online communities to understand the common questions and discussions related to the niche.
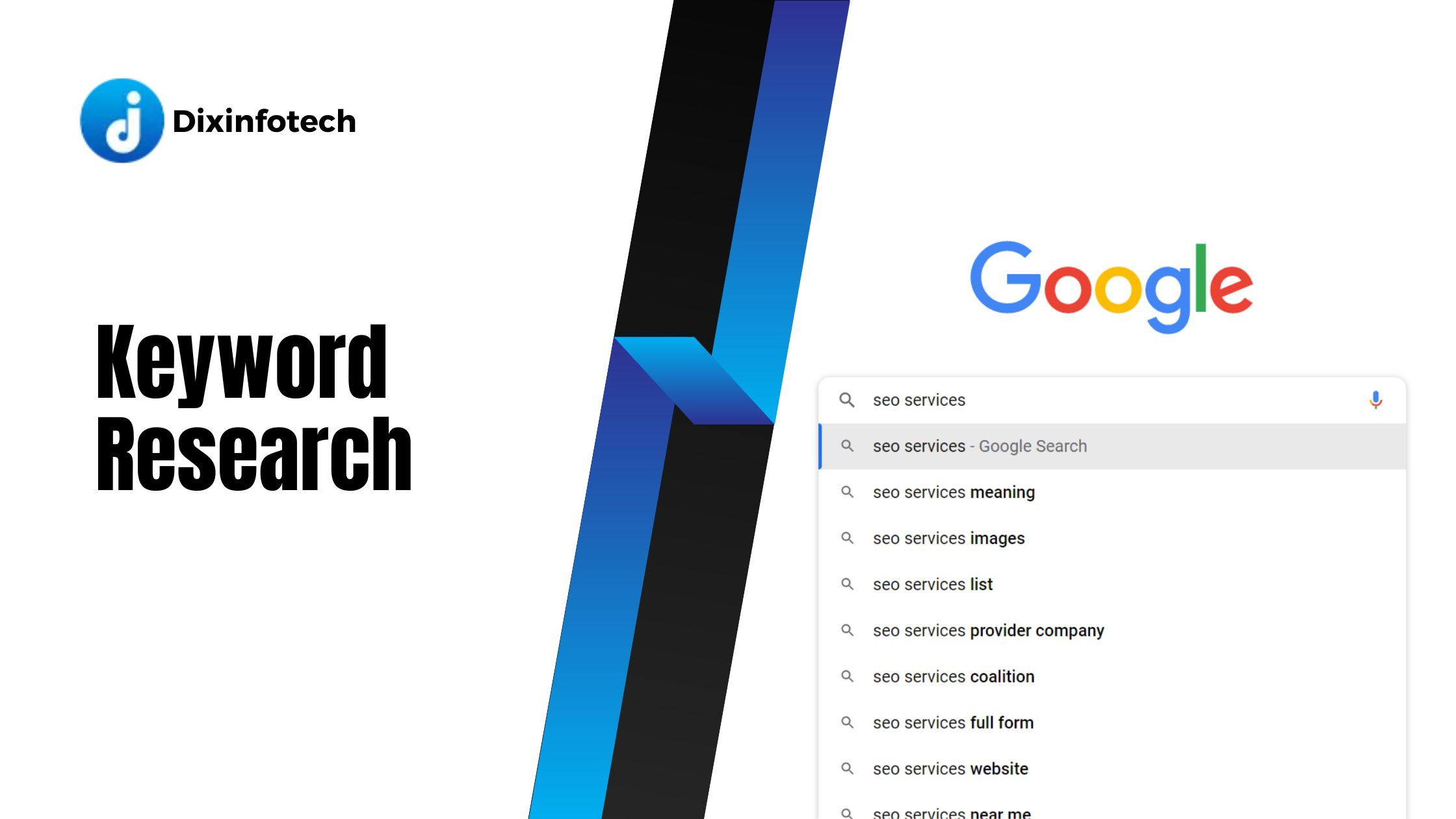
- Google Autocomplete and Related Searches: Utilize Google's Autocomplete feature and "Related Searches" section at the bottom of search results to discover additional keywords and phrases.
C. Utilizing keyword research tools
Keyword research tools can significantly assist in identifying relevant keywords, evaluating their search volume, competition, and other important metrics. Some popular keyword research tools include:
- Google Keyword Planner: A free tool that provides keyword ideas, search volume data, and keyword performance insights based on historical search data from Google.
- SEMrush: A comprehensive SEO tool that offers keyword research capabilities, competitive analysis, and other SEO-related features.
Ahrefs: Another robust SEO tool that provides keyword research, backlink analysis, and competitor research features.
Moz Keyword Explorer: A tool that offers keyword suggestions, search volume data, and difficulty scores to help prioritize keywords.
- Ubersuggest: A freemium tool that provides keyword ideas, search volume data, and keyword difficulty scores.
These tools can help website owners refine their keyword list, identify valuable long-tail keywords, and evaluate the competition for specific keywords. It's important to strike a balance between high search volume keywords and those with less competition to optimize the chances of ranking well in search results.
Title Tags
A. Writing unique and descriptive title tags
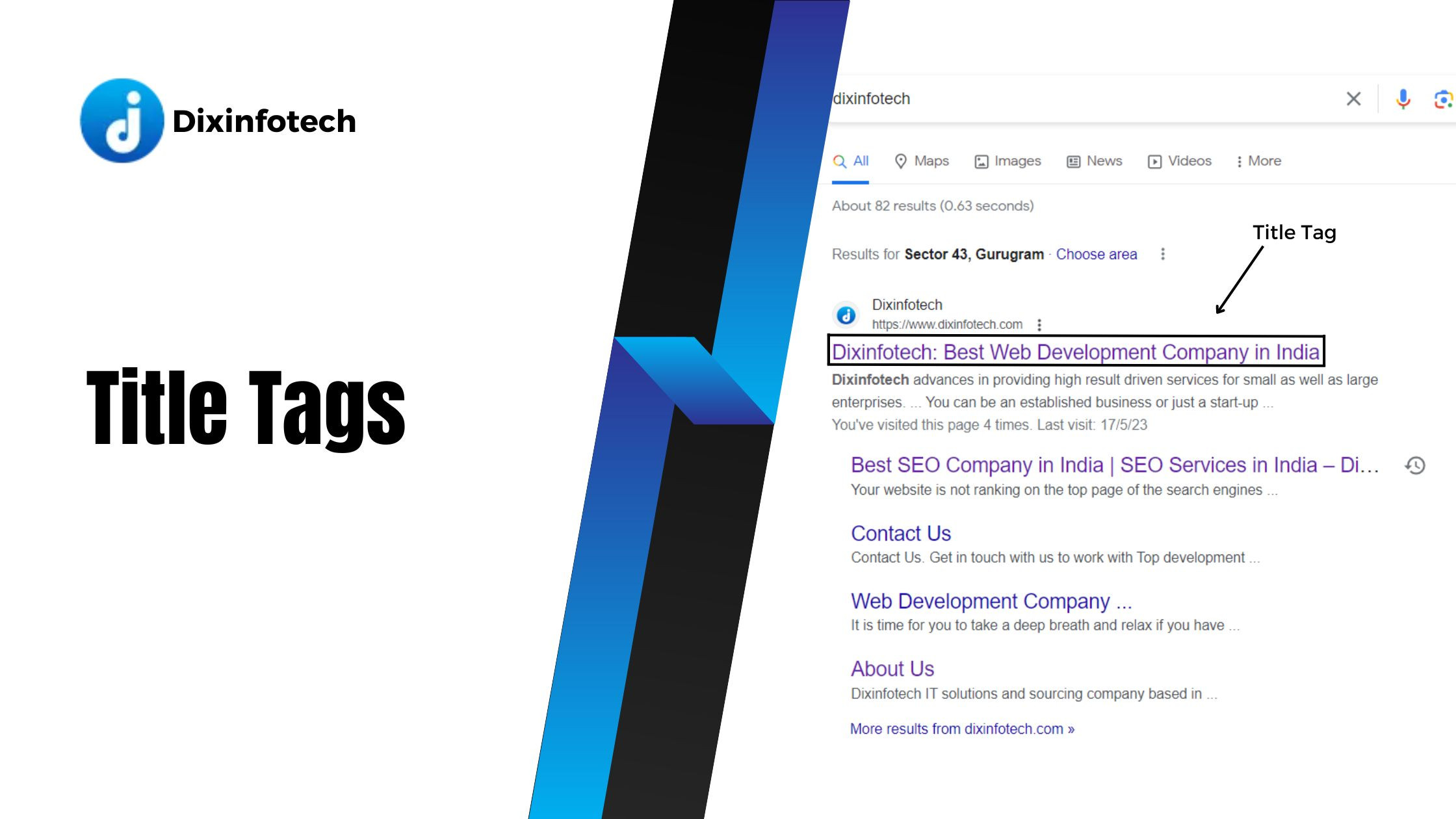
Title tags are HTML elements that define the title of a web page. They are displayed as clickable headlines in search engine results pages (SERPs) and are essential for both search engine optimization and user engagement. Here are some key considerations for writing effective title tags:
- Uniqueness: Each web page should have a unique title tag that accurately reflects its content. Avoid using duplicate or generic title tags across multiple pages, as this can confuse search engines and users.
- Descriptive: Title tags should provide a concise and accurate description of the page's content. Clearly convey the topic or purpose of the page to entice users to click on the search result.
- Relevant keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords that accurately represent the page's content and align with the target audience's search intent. However, avoid keyword stuffing or using irrelevant keywords solely for the purpose of optimization.
- Branding: Include the brand name, if applicable, in the title tag to enhance brand recognition and differentiate your website from competitors.
B. Including target keywords in title tags
Target keywords play a crucial role in optimizing title tags. By including relevant keywords, you increase the visibility and relevance of your web page for specific search queries. Here are some tips for incorporating target keywords effectively:
- Placement: Ideally, include the target keyword as close to the beginning of the title tag as possible. Search engines often prioritize the first few words when determining relevance.
- Variations: Consider using variations or synonyms of the target keyword to optimize for related search queries and capture a broader audience.
- Context: Ensure the target keyword fits naturally within the overall context of the title tag. It should make sense and accurately represent the page's content.
- Length: Be mindful of the recommended length for title tags, as excessively long titles may be truncated in search results. Aim to keep the title tag concise and informative while including the target keyword.
C. Keeping title tags within recommended length
It's important to adhere to the recommended length for title tags to ensure they are fully displayed in search engine results. While the exact character limit may vary across search engines, a general guideline is to keep title tags under 60 characters. Here's why length matters:
- Visibility: Longer title tags may get cut off in search results, potentially obscuring important information or keywords. By keeping the title tag within the recommended length, you maximize its visibility and readability.
- User experience: Clear and concise title tags make it easier for users to understand the content of your web page at a glance. This can enhance the user experience and encourage higher click-through rates.
- Mobile optimization: With the rise of mobile browsing, shorter title tags are especially crucial. Mobile devices have limited screen space, and shorter titles ensure that they are displayed properly and attractively on smaller screens.
- Focus and relevance: A shorter title tag forces you to prioritize the most important information and keywords. It encourages you to craft a more focused and relevant title that aligns with the page's content and user intent.
Meta Descriptions
A. Creating compelling meta descriptions
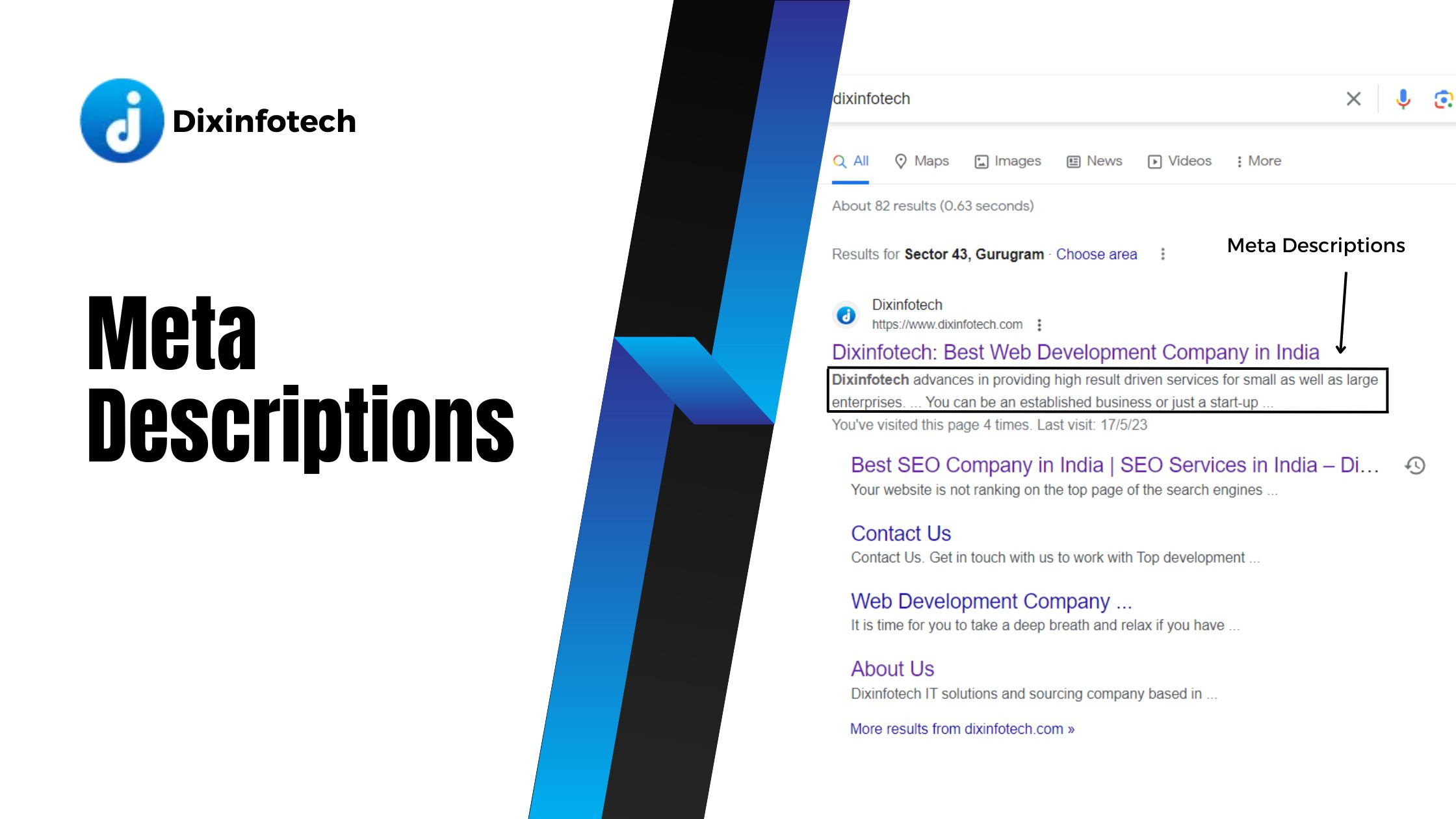
Meta descriptions are HTML attributes that provide a brief summary or preview of a web page's content. While they don't directly impact search engine rankings, well-crafted meta descriptions can significantly influence click-through rates and user engagement. Here are some tips for creating compelling meta descriptions:
- Conciseness: Keep meta descriptions concise, typically between 50-160 characters, to ensure they are fully displayed in search results. Use clear and compelling language to capture users' attention.
- Unique and specific: Craft unique meta descriptions for each page that accurately describe its content. Avoid duplicating meta descriptions across multiple pages, as this can lead to confusion and may affect search engine visibility.
- Call-to-action: Include a strong call-to-action (CTA) in the meta description to encourage users to click on the search result. Phrases like "Learn more," "Discover," or "Find out how" can entice users to visit your page.
- Benefits and value proposition: Highlight the key benefits or value proposition of the page's content. Explain what users can expect to find or achieve by visiting your page, addressing their needs or pain points.
B. Incorporating relevant keywords
While meta descriptions don't directly impact search engine rankings, incorporating relevant keywords can help improve their relevance and visibility. Here's how to effectively incorporate keywords in meta descriptions:
- Targeted keywords: Identify relevant keywords that align with the page's content and user search intent. Incorporate these keywords naturally in the meta description while ensuring it reads well and provides a clear message.
- Placement: Ideally, place important keywords toward the beginning of the meta description to make them more prominent. However, prioritize readability and ensure the description flows naturally.
- Synonyms and variations: Use synonyms and variations of target keywords to broaden the reach and capture a wider audience. This helps you appeal to users who may use different terms in their search queries.
C. Writing meta descriptions within recommended length
Meta descriptions should be written within the recommended length to ensure they are fully displayed in search results. While the exact character limit may vary across search engines, a general guideline is to keep meta descriptions under 160 characters. Consider the following when writing meta descriptions:
- Length considerations: Longer meta descriptions may get truncated in search results, potentially losing important information or CTAs. Aim to keep meta descriptions concise while conveying the main message effectively.
- Clarity and relevance: Focus on providing a clear and concise summary of the page's content within the character limit. Make sure the meta description accurately represents the page to set appropriate user expectations.
- Keyword inclusion: While it's important to include relevant keywords, ensure they fit naturally within the limited space. Avoid keyword stuffing or sacrificing readability for the sake of keyword optimization.
- Engagement and appeal: Craft meta descriptions that grab users' attention and entice them to click on the search result. Use persuasive language, highlight unique features, or address specific user needs to make your meta descriptions compelling.

Heading Tags
A. Using proper heading tags (H1, H2, etc.) to structure content
Heading tags, such as H1, H2, H3, and so on, are HTML elements used to structure and organize content on web pages. They not only provide visual cues for users but also play a significant role in search engine optimization. Here's how to use heading tags effectively to structure your content:
- H1 tag: Each web page should have a single H1 tag, which represents the main heading or the title of the page. The H1 tag should be descriptive and capture the overall topic or theme of the page.
- Subheadings: Use H2, H3, and subsequent heading tags to divide the content into logical sections or subtopics. This helps users navigate the page and improves readability.
- Hierarchical structure: Follow a logical hierarchy when using heading tags. Typically, the H1 tag represents the highest level, followed by H2, H3, and so on, in descending order. This hierarchy helps search engines understand the structure and importance of the content.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in the use of heading tags throughout the website. This creates a standardized structure and enhances user experience.
B. Including target keywords in heading tags
Including relevant keywords in heading tags can help signal the topic and relevance of your content to search engines. Here's how to incorporate target keywords effectively:
- H1 tag: Whenever possible, include the primary target keyword or a variation of it in the H1 tag. This helps search engines understand the main focus of the page.
- Subheadings: Incorporate related keywords or variations in subheadings (H2, H3, etc.), making sure they flow naturally and provide additional context to the content.
- Don't overdo it: While it's important to include keywords, avoid keyword stuffing or forcing them into every heading. Maintain a balance and prioritize readability and user experience.
C. Ensuring a hierarchy of headings
Maintaining a clear hierarchy of headings is essential for both user experience and search engine optimization. Here's why it matters:
Readability: Heading tags help users scan and understand the structure of your content quickly. A clear hierarchy improves readability and allows users to navigate to the sections that interest them.
Semantic structure: Search engines use heading tags to analyze the structure and context of your content. By following a logical hierarchy, you help search engines better understand the relationships between different sections of your page.
SEO impact: Properly structured heading tags can indirectly benefit your SEO efforts. When search engines recognize a well-organized hierarchy, they may attribute more relevance and importance to your content.
To ensure a proper hierarchy of headings:
- Start with H1: Begin each page with a single H1 tag that represents the main heading or title of the page.
- Use subheadings: Organize your content into logical sections and use H2, H3, and subsequent tags for subheadings.
- Avoid skipping levels: Maintain a consistent order without skipping heading levels (e.g., going from H2 to H4). This ensures a clear and understandable structure.
- Keep it concise: Use heading tags to summarize the content of each section briefly. Avoid lengthy headings that may confuse or overwhelm users.
URL Structure
A. Keeping URLs concise and descriptive
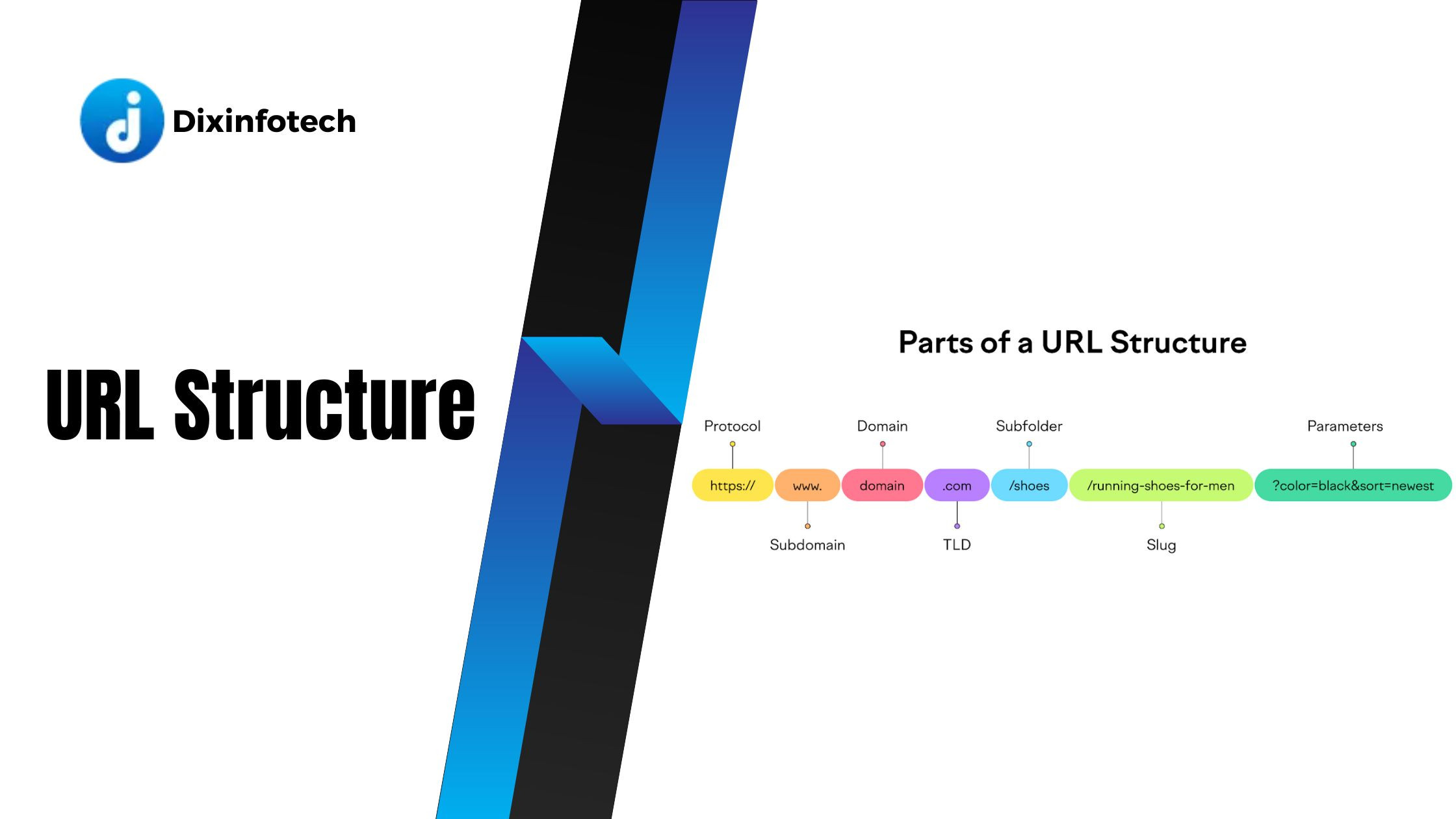
The structure of a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) plays a significant role in both user experience and search engine optimization. A well-crafted URL should be concise, descriptive, and provide users and search engines with a clear understanding of the page's content. Here are some tips for creating effective URL structures:
- Remove unnecessary elements: Keep URLs clean and concise by removing unnecessary parameters, session IDs, or other dynamic elements. Focus on the core elements that represent the page's content.
- Reflect the page's content: Incorporate relevant words or phrases in the URL that accurately describe the content of the page. Users should have an idea of what to expect by simply looking at the URL.
- Readability: Make URLs human-readable by using plain language and avoiding complex strings of numbers or characters. This enhances user understanding and improves the overall user experience.
B. Including target keywords in URLs
Incorporating relevant keywords in URLs can benefit search engine optimization by signaling the topic and relevance of the page's content. Here's how to include target keywords effectively:
- Primary keyword: Whenever possible, include the primary target keyword or a variation of it in the URL. This can help search engines understand the page's topic and potentially improve its visibility in relevant searches.
- Contextual keywords: Incorporate other relevant keywords or phrases that provide additional context and accurately represent the content of the page. However, avoid keyword stuffing or creating long, spammy URLs.
- Natural integration: Ensure that the keywords are integrated naturally into the URL. The URL should be readable and make sense to both users and search engines.
C. Using hyphens to separate words in URLs
When creating URLs, it is best practice to use hyphens ("-") to separate words. This is known as a "hyphenated URL structure" and offers several advantages:
- Readability and user experience: Hyphens improve the readability of URLs by clearly separating words. This makes it easier for users to understand the URL and its content.
- Search engine visibility: Search engines consider hyphens as word separators, which helps them recognize individual words in the URL. This can improve the URL's visibility in search engine results.
- Accessibility and shareability: Hyphenated URLs are more accessible, particularly for screen readers and assistive technologies. They also tend to be more shareable and user-friendly in various online platforms.
- Consistency and standardization: Using hyphens as word separators is a widely accepted convention in URL structures. It enhances consistency and makes URLs more intuitive for users.

Content Optimization
A. Creating high-quality and unique content
Creating high-quality and unique content is the foundation of successful on page SEO. Search engines value original, well-written content that provides value to users. Here are some guidelines for creating high-quality content:
- Unique and original: Ensure your content is unique and not copied from other sources. Plagiarized content can harm your website's reputation and rankings.
- Valuable information: Provide informative and valuable content that satisfies the user's search intent. Answer questions, solve problems, and offer insights that align with your target audience's needs.
- Well-researched: Conduct thorough research and provide accurate, up-to-date information in your content. Cite reliable sources and back up your claims with evidence.
- Engaging and well-written: Write in a clear, concise, and engaging manner. Use proper grammar, sentence structure, and formatting to enhance readability.
B. Including relevant keywords naturally in the content
Keywords play a crucial role in on page SEO. By including relevant keywords in your content, you improve its visibility and relevance to search engines. However, it's important to use keywords naturally and avoid keyword stuffing. Here's how to incorporate keywords effectively:
- Keyword research: Conduct thorough keyword research to identify relevant and valuable keywords related to your content. Consider the search volume, competition, and user intent when selecting keywords.
- Strategic placement: Include keywords in the page's title, headings, subheadings, and throughout the content. Distribute them naturally to ensure they fit contextually and don't disrupt the flow of the content.
- User-focused content: Prioritize the needs and interests of your target audience when incorporating keywords. The content should be informative and engaging for users, with keywords seamlessly integrated.
C. Using variations of target keywords
To broaden your reach and capture a wider audience, it's beneficial to use variations of target keywords. This approach helps you target different search queries and enhance the overall relevancy of your content. Consider the following:
- Synonyms and related terms: Identify synonyms, related terms, and alternative phrases that users may use in their search queries. Incorporate these variations naturally throughout your content.
- Long-tail keywords: Long-tail keywords are more specific and typically longer phrases. They often have less competition and can attract highly targeted traffic. Include relevant long-tail keywords in your content where appropriate.
- User intent: Consider the intent behind different search queries and align your content to address those intentions. Incorporate variations of keywords that cater to different user intents to provide a comprehensive and relevant content experience.
D. Paying attention to content length and readability
Content length and readability play crucial roles in user engagement and search engine optimization. Consider the following tips:
- Optimal length: Aim for a balance between comprehensive content and brevity. Longer articles tend to perform well in search results, but ensure the content remains focused and valuable. Avoid unnecessarily lengthy or thin content.
- Scannability: Use subheadings, bullet points, and paragraphs to break up the content and make it easily scannable for users. This improves readability and helps users find the information they need quickly.
- Readability and language: Write in a clear and accessible language that is easy for users to understand. Avoid jargon and overly complex terminology unless your target audience specifically requires it.
- Formatting: Use proper formatting techniques, such as bolding, italics, and lists, to highlight key points and improve readability. Make sure the content is visually appealing and easy to navigate.

Image Optimization
A. Using descriptive file names for images
When optimizing your on page SEO, it's important to pay attention to image optimization. The file names you choose for your images can have an impact on search engine visibility and user experience. Follow these guidelines for using descriptive file names:
- Relevant and descriptive: Choose file names that accurately describe the content or subject of the image. Use keywords or phrases related to the image to provide context.
- Use hyphens: Use hyphens to separate words within the file name. This improves readability and makes it easier for search engines to understand the meaning of the file name.
- Avoid generic names: Instead of generic names like "image1.jpg" or "photo123.png," be specific and provide meaningful names that reflect the image's content.
B. Optimizing alt text with target keywords
Alt text (alternative text) is a crucial element for image optimization. It provides a textual description of an image, which is useful for search engines and users who are visually impaired. Here's how to optimize alt text effectively:
- Descriptive and concise: Write alt text that accurately describes the image while keeping it concise. Use a few words to provide a clear understanding of what the image represents.
- Include target keywords: If relevant and appropriate, incorporate target keywords naturally into the alt text. However, avoid keyword stuffing or using keywords that are not directly related to the image.
- Accessibility considerations: Alt text is primarily intended to improve accessibility, so focus on providing information that would benefit visually impaired users. Use alt text to describe the content and purpose of the image in a way that is meaningful for those who cannot see it.
C. Compressing images for faster loading speed
Image file sizes can significantly impact the loading speed of your web pages, which is crucial for both user experience and SEO. Follow these tips to compress your images for faster loading:
- Image compression tools: Use image compression tools or plugins to reduce the file size of your images without compromising their quality. These tools optimize the image file by removing unnecessary data and compressing it for web use.
- Choose the right file format: Depending on the type of image, choose the appropriate file format. JPEG is typically suitable for photographs, while PNG is ideal for graphics or images with transparency.
- Resize images: Resize your images to the appropriate dimensions before uploading them to your website. Large images can slow down page load times, so ensure they are optimized for the specific space they will occupy.
- Test loading speed: Regularly test your website's loading speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. These tools can provide insights into areas where further optimization, including image compression, may be necessary.

Internal Linking
A. Creating a logical and hierarchical internal linking structure
Internal linking is the practice of linking pages within your own website. It plays a crucial role in on page SEO as it helps search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your website, distributes link authority, and improves user navigation. Follow these guidelines to create a logical and hierarchical internal linking structure:
Plan your website structure: Start by organizing your website's content into a logical hierarchy. Identify the main categories or sections and subpages that fall under each category.
Utilize main navigation: Use your website's main navigation menu to link to the primary pages or sections. This provides an easily accessible and consistent way for users to navigate your site.
Contextual linking: Within the content of your pages, link to other relevant pages on your website. Link to related topics, supporting articles, or more detailed information to provide additional value to users and search engines.
Deep linking: Link to deeper pages within your website, not just the homepage or top-level pages. This spreads link authority throughout your site and helps search engines discover and index more of your content.
B. Using anchor text with relevant keywords
Anchor text is the clickable text within a hyperlink. It's important to optimize anchor text to provide both search engines and users with relevant information about the linked page. Consider these best practices for using anchor text with relevant keywords:
- Relevant and descriptive: Use anchor text that accurately describes the linked page. It should provide users with a clear understanding of what they can expect when they click the link.
- Incorporate keywords naturally: When appropriate, include relevant keywords in your anchor text. However, avoid excessive keyword usage or over-optimization, as it may appear unnatural and spammy.
- Avoid generic phrases: Instead of using generic phrases like "click here" or "read more," use anchor text that reflects the topic or context of the linked page. This helps both users and search engines understand the relevance of the link.
C. Ensuring all internal links are working properly
Regularly checking the functionality of your internal links is essential to provide a seamless user experience and maintain good SEO practices. Follow these steps to ensure all internal links are working properly:
Conduct regular audits: Perform periodic audits of your website to identify any broken or redirected internal links. Several online tools can help you identify broken links, such as Google Search Console or website crawlers.
Fix broken links: When you discover broken links, update or fix them as soon as possible. Update the link URL if the page has been moved or remove the link if the page no longer exists.
Use proper redirects: If you've made changes to your website's URL structure or moved content, use proper redirects (301 redirects) to ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct page.
Monitor changes and updates: Keep track of any changes or updates you make to your website's content and internal links. Regularly review and test the links to ensure they are functioning correctly.

Page Loading Speed
A. Optimizing images and videos for faster loading
Images and videos are often the largest files on a web page, and optimizing them can significantly improve page loading speed. Consider the following techniques for optimizing media files:
- Image compression: Use image compression tools to reduce the file size of images without compromising their quality. This reduces the time required to transfer the images to the user's browser.
- Proper image formats: Choose the appropriate image format based on the content. JPEG is suitable for photographs, while PNG is ideal for graphics and images with transparency. Use SVG for vector-based graphics.
- Lazy loading: Implement lazy loading techniques to delay the loading of images and videos until they are visible in the user's viewport. This speeds up initial page loading and improves overall performance.
- Video optimization: Compress videos using codecs that maintain a balance between quality and file size. Consider using video formats such as MP4 and WebM, and use video players that support adaptive streaming.
B. Minifying CSS and JavaScript files
Minifying CSS and JavaScript files involves removing unnecessary characters like white spaces, line breaks, and comments, reducing their file size and improving loading speed. Follow these steps to minify your CSS and JavaScript files:
- Manual minification: Remove unnecessary white spaces, line breaks, and comments from your CSS and JavaScript files using a text editor or specialized minification tools.
- Automated minification: Utilize minification tools or plugins that automatically minify your CSS and JavaScript files during the build or deployment process. This simplifies the optimization workflow and ensures consistency.
- Combine files: Minify and combine multiple CSS and JavaScript files into a single file. This reduces the number of HTTP requests required to load the page, improving loading speed.
C. Enabling browser caching
Browser caching allows the temporary storage of web page resources, such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files, on the user's browser. Enabling caching can significantly improve page loading speed for returning visitors. Follow these steps to enable browser caching:
Set expiration headers: Configure your web server to include proper expiration headers in the HTTP response. This tells the browser how long it can cache specific resources before requesting them again.
Use cache-control directives: Implement cache-control directives, such as "max-age" and "public," to instruct the browser on caching behavior. This allows resources to be cached and served from the browser's cache, reducing server requests.
Versioning or fingerprinting: Append version numbers or unique fingerprints to the URLs of static resources. This ensures that when changes are made to those resources, the browser requests the updated versions instead of relying on cached versions.
D. Using a content delivery network (CDN)
A content delivery network (CDN) is a network of servers distributed geographically that stores cached copies of your website's static files. Using a CDN can significantly improve page loading speed by delivering content from servers located closer to the user. Consider these steps for using a CDN:
Choose a reliable CDN provider: Select a reputable CDN provider that has a widespread network of servers and offers good performance and reliability.
Configure your CDN: Set up your CDN by configuring it to cache and deliver your static files, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files.
Implement CDN URLs: Modify the URLs of your static resources to point to the CDN instead of your original server. This ensures that when users request those resources, they are delivered from the CDN's servers.

Mobile-Friendliness
A. Ensuring responsive design for mobile devices
With the increasing use of mobile devices for browsing the internet, it's crucial to ensure that your website has a responsive design. Responsive design allows your website to adapt and display correctly on various screen sizes and devices. Consider the following practices for achieving a responsive design:
Fluid layouts: Use fluid or flexible grid systems that automatically adjust content and elements based on the screen size. This ensures that your website looks good and remains readable across different devices.
Media queries: Implement CSS media queries to apply specific styles and layouts based on the device's screen size. This allows you to optimize the visual appearance and user experience for different devices.
Mobile-first approach: Start designing your website with mobile devices in mind, focusing on the most critical content and functionalities. Then progressively enhance the design for larger screens.
B. Testing and optimizing for different screen sizes
To provide a seamless mobile experience, it's important to test and optimize your website for different screen sizes. Follow these steps to ensure your website looks and functions well on various devices:
Device testing: Test your website on different mobile devices with various screen sizes, including smartphones and tablets. This helps identify any layout or functionality issues specific to certain devices.
Responsive testing tools: Use online responsive testing tools that simulate different device screens. These tools allow you to preview and interact with your website as it would appear on various devices.
User testing: Conduct user testing sessions with individuals using mobile devices to browse your website. Gather feedback and insights to understand how users navigate and interact with your mobile interface.
C. Using mobile-friendly navigation and buttons
Mobile users have different interaction patterns compared to desktop users. Optimizing your navigation and buttons for mobile devices enhances the mobile-friendliness of your website. Consider these best practices:
Clear and concise navigation: Simplify your website's navigation menu for mobile devices. Use clear labels and consider using collapsible menus or hamburger menus to save screen space.
Finger-friendly buttons: Ensure that buttons and interactive elements are large enough and have sufficient spacing to be easily tapped with a finger. This reduces the chances of accidental taps and improves user experience.
Touch gestures: Incorporate touch-friendly gestures, such as swiping or scrolling, for smooth navigation on mobile devices. Use these gestures to enhance user interactions and make the browsing experience intuitive.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): Consider implementing AMP, a framework designed to create fast-loading web pages specifically for mobile devices. AMP optimizes the performance and speed of your mobile web pages, improving the overall mobile experience.
By ensuring responsive design, testing and optimizing for different screen sizes, and using mobile-friendly navigation and buttons, you can create a mobile-friendly website that provides an optimal experience for users on various devices. This improves user engagement, reduces bounce rates, and positively impacts your search engine rankings, as search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites.

User Experience
A. Making content easy to read and understand
When it comes to on page SEO, user experience plays a crucial role in determining the success of your website. By making your content easy to read and understand, you can enhance the user experience and encourage visitors to stay on your site longer. Consider the following practices:
Use clear and concise language: Write in a way that is easy for your target audience to comprehend. Use simple and straightforward language, avoiding excessive jargon or technical terms.
Break content into sections: Organize your content into logical sections with headings, subheadings, and bullet points. This helps users scan and navigate your content easily, improving readability.
Use legible typography: Choose fonts that are easy to read, both on desktop and mobile devices. Use an appropriate font size, line spacing, and contrast between text and background to ensure readability.
B. Improving website navigation and usability
A well-structured and user-friendly website navigation enhances the overall user experience. It helps visitors find the information they're looking for quickly and efficiently. Consider the following tips to improve website navigation and usability:
Clear and intuitive navigation menus: Ensure that your navigation menus are clearly labeled and placed prominently on your website. Use logical categorization and keep the menu options concise.
Implement a search function: Include a search bar on your website to allow users to search for specific content or products. Ensure that the search function is prominently visible and provides accurate and relevant results.
Consistent design and layout: Maintain consistency in the design and layout across your website. This includes the placement of elements, color schemes, and overall visual style. Consistency helps users navigate your site with ease.
User-friendly URLs: Use descriptive and user-friendly URLs that give visitors an idea of what to expect when they click on a link. Avoid using complex or lengthy URLs that are difficult to read and remember.
C. Reducing bounce rate and increasing user engagement
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page. To reduce bounce rate and increase user engagement, consider the following strategies:
- Relevant and engaging content: Create high-quality and relevant content that captures the interest of your target audience. Use engaging visuals, compelling headlines, and a conversational tone to keep visitors engaged.
- Internal linking: Incorporate internal links within your content to guide users to related articles or pages on your website. This encourages them to explore more of your content and reduces the likelihood of bouncing.
- Call-to-action (CTA) buttons: Include clear and enticing CTAs throughout your website to prompt users to take specific actions. Whether it's signing up for a newsletter, making a purchase, or sharing content, well-placed CTAs can increase engagement.
- Optimize page load speed: As mentioned earlier, ensure your website loads quickly. A slow-loading website can lead to higher bounce rates. Compress images, minify code, and utilize caching techniques to improve page load speed.
By focusing on making your content easy to read, improving website navigation and usability, and reducing bounce rate while increasing user engagement, you can enhance the overall user experience of your website. This not only improves your chances of higher search engine rankings but also increases the likelihood of visitors returning to your site and becoming loyal users.

Monitoring and Testing
A. Using web analytics tools to track performance
Monitoring the performance of your on page SEO efforts is essential for understanding how your website is performing and identifying areas for improvement. Web analytics tools provide valuable insights into user behavior, traffic sources, conversion rates, and more. Consider the following practices:
Install web analytics software: Set up a web analytics tool, such as Google Analytics, on your website. This allows you to track key metrics like page views, bounce rates, average time on page, and user demographics.
Analyze user behavior: Dive into the data provided by web analytics tools to gain insights into how users interact with your website. Identify popular landing pages, exit pages, and conversion funnels to optimize user flow.
Monitor organic search traffic: Track the organic search traffic to your website and monitor changes over time. Identify which keywords are driving the most traffic and focus on optimizing those pages further.
B. Conducting A/B tests to improve conversions
A/B testing, also known as split testing, allows you to compare two versions of a web page to determine which one performs better in terms of user engagement and conversions. By conducting A/B tests, you can make data-driven decisions and optimize your on page SEO strategies. Consider the following steps:
- Identify a specific goal: Determine what specific aspect of your web page you want to test and improve. This could be the headline, call-to-action buttons, form design, or layout.
- Create two variations: Develop two different versions of the web page, with only one element (e.g., headline, button color) being different between them. Keep all other factors constant.
- Split traffic evenly: Use an A/B testing tool to divide your website traffic equally between the two versions of the web page.
- Measure and compare results: Monitor the performance of both versions and compare key metrics such as conversion rate, bounce rate, or average time on page. Analyze the results to determine which variation performs better.
- Implement the winning variation: Once you have statistically significant results, implement the winning variation as the new default version on your website.
C. Regularly reviewing and updating on page SEO strategies
On page SEO is an ongoing process that requires regular review and updates to stay relevant and effective. Search engine algorithms and user behaviors evolve over time, so it's important to adapt your strategies accordingly. Consider the following practices:
- Stay updated on SEO best practices: Keep yourself informed about the latest SEO trends, algorithm updates, and industry insights. Follow reputable sources, attend conferences, and engage in online communities to stay up to date.
- Audit and optimize existing content: Regularly review your existing content to ensure it aligns with current SEO practices. Optimize meta tags, headings, keywords, and content structure as needed to improve visibility and user experience.
- Explore new keyword opportunities: Continuously conduct keyword research to identify new keyword opportunities and search trends. Update your content strategy to target relevant keywords that have the potential to drive more traffic.
- Test and refine on-page elements: Experiment with different on-page elements, such as headings, internal linking, or multimedia content, to improve user engagement and SEO performance. Monitor the results and make adjustments based on data-driven insights.
- Analyze competitor strategies: Keep an eye on your competitors and analyze their on page SEO strategies. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and use this information to refine your own strategies and gain a competitive edge.
By regularly monitoring your website's performance, conducting A/B tests, and reviewing and updating your on page SEO strategies, you can ensure that your website remains optimized for search engines and provides an excellent user experience. This iterative process allows you to continuously improve your rankings, attract more organic traffic, and achieve better
Conclusion
A. Recap of key points for on page SEO
In this guide, we've covered the basics of on page SEO and its importance for better search engine rankings. Let's recap the key points we've discussed:
On page SEO refers to optimizing various elements on your website to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results.
Conduct thorough keyword research to understand your target audience's search intent and identify relevant keywords to optimize your content around.
Pay attention to title tags, meta descriptions, heading tags, URL structure, and content optimization to make your web pages more appealing to both search engines and users.
Optimize images by using descriptive file names, relevant alt text, and compressed file sizes to enhance page loading speed.
Internal linking helps establish a logical structure, improves navigation, and distributes link authority across your website.
Focus on page loading speed by optimizing images, minifying code, enabling browser caching, and using content delivery networks (CDNs).
Ensure your website is mobile-friendly, with responsive design, testing for different screen sizes, and mobile-friendly navigation.
Prioritize user experience by making content easy to read, improving navigation, and reducing bounce rates while increasing user engagement.
Monitor and track your website's performance using web analytics tools, conduct A/B tests to optimize conversions, and regularly review and update your on page SEO strategies.
B. Emphasizing the ongoing nature of on-page SEO optimization
It's important to recognize that on-page SEO is an ongoing process. Search engine algorithms evolve, user behaviors change, and new trends emerge. Therefore, optimizing your website's on-page elements should be seen as a continuous effort.
Regularly monitor your website's performance, analyze user behavior, and adapt your strategies accordingly. Stay updated with the latest SEO best practices, industry trends, and algorithm changes to ensure that your website remains relevant and competitive.
C. Encouraging continuous learning and adaptation to algorithm changes
Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving to provide users with the best possible search results. To stay ahead of the competition and maintain your rankings, it's crucial to engage in continuous learning and adapt your on-page SEO strategies accordingly.
Stay informed about the latest SEO developments, attend industry conferences, participate in online communities, and engage with reputable sources. This proactive approach will help you stay on top of algorithm changes and make informed decisions to improve your website's visibility and search engine rankings.
Remember, on-page SEO is just one piece of the overall SEO puzzle. It works in conjunction with other SEO practices, such as off-page optimization and technical SEO, to achieve the best results. By implementing the principles discussed in this guide and continuously refining your on-page SEO strategies, you can increase your website's visibility, attract more organic traffic, and ultimately improve your search engine rankings.













